The success or failure of crabs raised in net enclosures on tidal flats largely depends on the strength of the facilities against wind and waves, as well as the effectiveness of escape prevention measures. Therefore, farmers must conduct daily patrols to monitor conditions. After each low tide, they should check for signs of water seepage or leakage in the earth dam, inspect whether the fence posts have collapsed, and ensure the netting remains intact. Any damage found should be repaired immediately, especially since blue crabs are most active at night and may attempt to escape during this time.
During high tides, the nets can become easily disturbed, increasing the risk of crabs escaping. When the tide rises over the dam, blue crabs tend to gather around the fence. If there is a hole or tear in the net, groups of crabs may take the opportunity to flee. At such times, immediate repairs are essential to prevent large-scale losses.
Additionally, when water quality in the small tidal pool becomes poor, crabs are more likely to burrow into the mud and escape. This situation also needs close attention. The main predators of the net-enclosed crabs include tigerfish, Chinese pond frogs, and fingerlings of certain fish species. These predators often attack during the crab molting period, which is a vulnerable time for the crabs.
To manage this, during breeding periods, farmers can expose the crabs to the tides during each cycle. By draining the pool slightly, they can capture and remove the predators. However, it's important to leave pelicans and pike in the pool, as they help clean up sludge and leftover food at the bottom. These species can coexist peacefully with the green crabs, contributing to better water quality and even boosting overall production.
Melting point 260 °C
Boiling point 91°C
density 0.868 g/mL at 25 °C
vapor density 1.6 (vs air)
vapor pressure <0.1 mm Hg ( 20 °C)
storage temp. Store at R.T.
solubility Soluble in ethanol and methanol.
form Liquid
PH 13 (5g/l, H2O, 20℃)
Water Solubility Miscible
Stability: Reacts violently with acids, water. Incompatible with chlorinated solvents, moisture. Absorbs carbon dioxide from the air. Highly flammable.
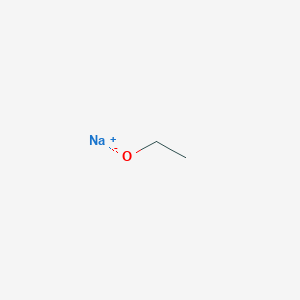
Sodium Ethoxide CAS No.141-52-6
Sodium Ethoxide Basic Information
CAS: 141-52-6
MF: C2H5NaO
MW: 68.05
EINECS: 205-487-5
Mol File: 141-52-6.mol
Sodium Ethoxide Structure
Melting point 260 °C
Boiling point 91°C
density 0.868 g/mL at 25 °C
vapor density 1.6 (vs air)
vapor pressure <0.1 mm Hg ( 20 °C)
storage temp. Store at R.T.
solubility Soluble in ethanol and methanol.
form Liquid
PH 13 (5g/l, H2O, 20℃)
Water Solubility Miscible
Stability: Reacts violently with acids, water. Incompatible with chlorinated solvents, moisture. Absorbs carbon dioxide from the air. Highly flammable.
Sodium Ethoxide,Sodium Ethoxide Formula,Sodium Ethoxide Structure,Sodium Methoxide Formula,Sodium Ethoxide In Ethanol Oxide Density
Shandong YingLang Chemical Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com