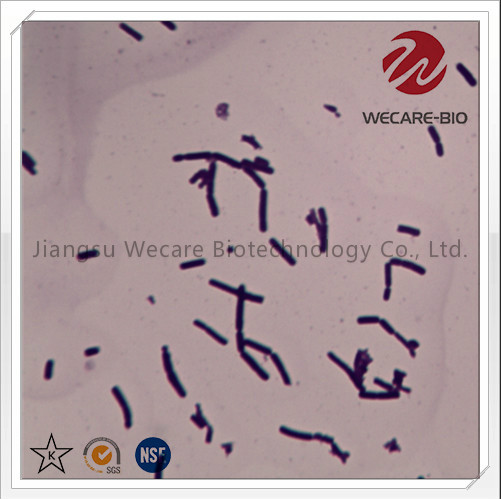
All Probiotic stains were made by food grade Natural organic raw materials; We assure pesticides, antibiotics and GMO are free, and the concentration of heavy metal is lower than the international standards. Our utmost aim is to share our production experience and research with our customers. Before and after sales, we help our customers complete works including design, pilot, raw material procurement, testing and production.
*Related Products:Probiotic Private Label, Ts6 Probiotic ,Names Probiotics,Probiotics Raw Material,prebiotics probiotics.
Probiotic,Bifidobacterium Spp,Leuconostoc Spp,Probiotic Private Label,Ts6 Probiotic,Names Probiotics,Probiotics Raw Material
JiangSu Wecare Biotechnology Co., Ltd. , http://www.wecare-life.com