The environmental humidity in the southwestern mountainous areas of China is relatively large. When the temperature in winter is lowered, it is easy to reduce the body temperature of the cattle, resulting in slow growth of fattening cattle, lower feed compensation, abortion of pregnant cows, and reduced survival rate of yak weaning. The economic benefits of local beef cattle breeding. Let's study the wintering management techniques of beef cattle in the southwest mountainous area.
First, the cow house insulation and ventilation
Beef cattle have different temperature requirements at different growth stages, and cattle have the best performance in the optimal temperature range. The room temperature requirements for different barns are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Room temperature requirements for different barns
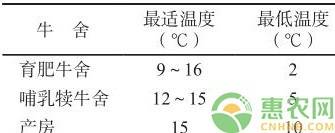
It can be seen from Table 1 that when the temperature of the fattening barn is below 2 °C, the cow body will emit a lot of energy to maintain body temperature, reduce weight gain, and reduce the body's immune resistance. Therefore, it is especially important to maintain the proper ambient temperature of the cattle during the winter. Specific practice: the roof of the barn is tightly rigged, and there are no wind tunnels on the four walls (to prevent the thief from invading), and the doors and windows are draped to keep the temperature of the barn as low as possible within the lower limit of the optimum temperature. Keep the airy windows ventilated, cover the shelter, and use the light. The cow mattress material can be used with hay, dry straw, soft straw, etc. All the padding is mixed into the heat-absorbing and hygroscopic materials such as sawdust and furnace ash, and the water in the cow house is removed in time to ensure the grass, the grass, the cleaning, and the diligence. In addition to the feces, pay attention to the thick padding (not less than 12 cm), keep the litter dry, and improve the body temperature of the cow. In the perinatal cow barn and the newborn yak barn, pay attention to warming, change the straw and other litter, and increase the thickness (not less than 15 cm). Conditional cattle farms can be equipped with infrared heating lamps or heaters.
In the winter, the cow house should keep in mind that the air in the house is smooth and fresh, and the necessary ventilation is required to open the door and window when the temperature is relatively high at noon. Generally, the ammonia in the air of the barn should be less than 20 microliters / liter, the hydrogen sulfide should be less than 10 microliters / liter, and the carbon dioxide should be less than 0.25%.
Second, feed nutrition
(1) Optimizing the concentrate formula
The body temperature of beef cattle is generally maintained at around 38.5 °C. The winter is cold and cold, and the heat loss of the cattle body is accelerated. In order to maintain a constant body temperature, the body will use more energy and the energy demand for the feed will increase. To this end, the winter concentrate formula needs to be adjusted, the proportion of energy raw materials such as corn is appropriately increased, and the proportion of protein raw materials such as soybean meal, rapeseed meal, cotton aphid, DDGS, etc. is reduced, and the addition of low-energy raw materials of bran is reduced.
The addition of high-energy oils to concentrates is the best way to improve the energy level of concentrates, but the following points should be noted: First, to ensure the safety of disease prevention and control (such as mad cow disease), it is forbidden to add animal-derived oils such as butter and sheep. Oil, etc. The second is vegetable oils, such as rapeseed oil, soybean oil, etc., the amount of addition needs an appropriate amount, in the wintering feeding conditions based on concentrate, the amount of vegetable oil is generally not more than 3%. This is because vegetable oils are rich in unsaturated fatty acids, enter the rumen and hydrogenate into saturated fatty acids under the action of microorganisms and then enter the intestines for emulsification and digestion and absorption; rumen microorganisms can only hydrogenate 3% of dry matter oils, if plant oils are added Excessive, unhydrogenated unsaturated fatty acids are toxic to microorganisms such as ciliates in the rumen, thereby affecting normal rumen fermentation and digestive functions. The third is to add a higher dose of vegetable oil, need to add appropriate amount of calcium carbonate (feed dry matter containing 0.9% ~ 1% calcium), which is conducive to fatty acid calcification, can reduce the degradation of fatty acids in the rumen, increase the proportion of rumen, maintain normal rumen Features. Fourth, under conditions, large doses of rumen-protective fat can be added because the rumen-protective fat is stabilized in some way in the rumen, is not hydrolyzed by rumen microorganisms, and does not affect the activity of rumen microorganisms. Through the rumen directly into the stomach and small intestine for digestion and utilization, to provide energy for the body of cattle; the general protective fat is fatty acid calcium, hydrogenated fat and rumen stable fat three types. The fifth is to add oilseed raw materials, such as rapeseed, sesame seeds, etc., to the whole grain or flattened feeding, which can largely avoid the degradation of oil in the rumen and improve the efficiency of rumen.
Due to the lack of green and green feed in winter, it is easy to cause the lack of vitamins and trace minerals in beef cattle. At the same time, the major mineral elements such as sodium, calcium and phosphorus need to be added. The cattle farmers can purchase premixes at different stages of beef cattle (including the nutritional needs). Vitamins, traces and minerals are used to prepare concentrates. Premix sizes are generally within 5% (ie 5 kg premix is ​​required to prepare 100 kg of concentrate). Because the rumen is not yet developed and sound, the digestion and absorption capacity is weak, and the nutritional requirements and feed preparation technology level are high. It is recommended to use the yak feed produced by regular manufacturers to improve the survival rate of weaning and promote growth and development.

(2) Guarantee the supply of roughage
1. Conventional roughage winter reserve
There are limited types of forage in winter, lack of green feed, and the storage of roughage is required. In the absence of green grass supplements, a medium-sized bovine (body weight 300-400 kg) requires at least 1,500 kg of roughage such as green hay, straw, and silage corn stalks for winter. The roughage feed should be as short as 2 to 3 cm, which is good for digestion and absorption. You can also use the distiller's grains to make some roughage supplements, but the distiller's grains can't be used for pregnant cows to avoid miscarriage; in general, the amount of distiller's grains accounts for half of the supplemented roughage. In order to prevent rumen acidosis caused by distiller's grains, 1% should be added to the roughage. ~ 2% baking soda.
2. Planting high quality pasture
When the cattle farm grows its own grass, it can plant suitable high-quality pastures in the autumn to supplement the shortage of winter green grass and green grass according to the local altitude and microclimate. Artificial grass can be sown in a single type of pasture or mixed with various pastures. It is recommended to use suitable leguminous grasses (such as white clover, alfalfa, etc.) and gramineous pastures (such as ryegrass, Dactylis, foxtail, etc.) when mixing, which is due to the nitrogen fixation of legumes on soil. Undergraduate forage grows, while the leguminous forage has higher protein content, and the gramineous forage has higher sugar content. The seed dosage of mixed leguminous grasses and grasses is more suitable for 3:1. Beef cattle are fed with such mixed pastures, and the nutritional mix is ​​suitable. For example, in the middle and low-altitude agricultural areas and mild and moderate rocky desertification areas in the southwest mountainous areas, the perennial ryegrass, Dactylis and white clover can be planted or planted in grasses and legumes, and perennial ryegrass. The seed dosage of Dactylis glabra L. and White Clover is 4:3:3, the seeding amount of the seeding is 1.5-2 kg/mu, the sowing seeding amount is 2.5-3 kg/mu, and the stubble height is 5-8 cm.
3. Straw silage treatment
The crop straw in the agricultural area of ​​the southwest mountainous area is mainly corn stalk, straw, corn cob, etc., and can be fully utilized as roughage for cattle. Corn stalks and straw are harvested during harvesting of corn and rice. The green leaves are more, the degree of lignification is lower, and the nutritional value is higher. Because of the high water content (about 60%), silage preservation is required. The silage material is as short as 4 to 7 cm, and is filled into silage. According to the moisture content of the raw material, the amount of water is added, and the water content is adjusted to 60% to 65%. A simple method for judging the water content of silage raw materials: take a chopped and compacted corn stover or straw for sputum, and then hold it firmly in the hand. If there are water drops on the fingers, but not in the series, the raw materials are included. The amount of water is appropriate. The raw materials are filled 20 to 30 cm thick, and need to be evenly divided and laminated, and evenly spray silage additives or lactic acid bacteria preparations, which is beneficial to the formation of silage anaerobic environment, shortening silage time and improving silage success rate. Silage is a very time-sensitive job. After it has been stored (窖), it should be quickly sealed. Where conditions permit, high-powered mowers, tumbler machines and silage baling machines can be purchased. During the harvest season of silage corn stalks, it is best to use the local rural labor resources to silage corn stalks to the silage corn producing areas. Harvesting, shortening, frustration, bundling, and encapsulation are closed. The successful silage is yellow-green, has a sour taste, has good palatability, and the nutritional value has been further improved.
(3) Properly increase the proportion of feeding of refined and coarse feed
Under the conditions of low temperature and cold and cold environment in winter, the energy produced by the rumen fermentation of cattle is transferred to maintain the body temperature of the cattle, and the cattle maintain a corresponding increase in nutrition, which is generally 10% to 15% higher than the feeding standard. Therefore, in winter, it is necessary to increase the concentrate of 10% to 15% to improve the proportion of refined and coarse feed, so as to maintain and enhance the production performance of cattle weight gain, milk production and reproduction. Under normal circumstances, in the winter, the feeding can be increased once in the evening, and the daily feeding amount of the concentrate should be increased by 10% to 15%. Fine roughage should be protected from wind, rain and snow to ensure that the feed is not mildewed and frozen. When silage corn stalks, straw, etc. are used as the main roughage, the refined roughage reaches 5:5 than the recommended growth, the pregnant cows reach 4:6, and the fattening cattle reach 6:4.

Third, feeding management
(1) Guarantee drinking water temperature and safety
Winter should provide warm water for cattle, which is conducive to their growth and milk production. The drinking water temperature of adult cattle is controlled at 9-15 °C, and the calf is 35-38 °C. Drinking water is mainly derived from tap water, and deep well water and river water are only allowed to be drinked after being precipitated and disinfected. It is forbidden to supply water that is mildewed and deteriorated. Although the amount of water consumed by beef cattle in winter is relatively small, it still needs to be supplied. One cow consumes 5% of the body weight per day, which is 3-4 times that of dry matter.
(2) More sun and brushing the body
When the weather is good, after the daily feeding, let the beef cattle get more sun, can promote the synthesis of vitamin D, which is beneficial to the health of the bones; at the same time, brushing the cattle body can prevent the occurrence of skin diseases and ectoparasites. It can promote blood circulation of cattle and improve cold and cold resistance.
(3) Early breeding and miscarriage
After the cattle are mated, the appetite is enhanced, the feed intake is increased, and the body is easy to deposit fat, which can play a role in protecting the cold. Therefore, adult cows are mated in the second sex period after childbirth, and the reserve cows are bred at 16 months of age to facilitate wintering.
Winter cows eating spoilage or frozen feed, malnutrition, slipping, etc. are all important causes of miscarriage. Therefore, it is especially important for pregnant cows to have abortion in winter. It is recommended to do the following four points: First, meet the nutritional needs of pregnant cattle. In addition to maintaining the life activities of pregnant cattle, the nutritional needs of the late pregnancy must also meet the rapid growth and development of the fetus. It is necessary to feed the crude feed that meets the nutritional needs and to grasp the sensation of the late pregnant cattle. In order to ensure the stable nutritional balance of pregnant cows, do not suddenly change the feed, and feed on the principle of “timed quantitative, first coarse and fineâ€. The second is to feed loose and delicious feed. In the late pregnancy, the fetus grows rapidly, the uterus expands, and the extrusion force of various organs is enhanced. It is necessary to feed the pregnant cows with some bran-type loose feed, and at the same time reduce the amount of rough feed and ensure the normal fetus. Growth and development, reduce the pressure on the organs, ensure smooth blood circulation, and prevent miscarriage. During the labor period, pregnant cows are fed with small, good quality, digestible and delicious feed. It is strictly forbidden to feed the distiller's grains. The third is proper exercise. Pregnancy cows consume a lot of nutrients, are prone to weakness, and have reduced resistance, so regular exercise is required. In winter, the road is cold and slippery, to prevent rushing and running. In the later stages of pregnancy, do not climb the mountain, do not take steep slopes and dangerous roads, do not take the ice slides, and prevent slipping. Fourth, pregnant cows should be kept separately from other animals and managed separately to prevent biting, topping and squeezing to ensure the safety of pregnant cows and avoid miscarriage.
(4) Strengthening the management of yak breeding
The yak's tissue and organs have not yet fully developed, and it has poor resistance to the surrounding adverse environment, the nervous system is underdeveloped, the body temperature regulation ability is poor, and the digestive function is weak. The extensive feeding management is likely to cause the birth of the newborn yak. In the wet and cold winter in the southwest mountainous area, it is more important to strengthen the management of yak breeding. It is recommended to do the following three things: First, break the umbilical cord as soon as possible and clear the mucus. Usually, the umbilical cord of the yak will be naturally torn off, but in the wet and cold winter, in order to keep the newborn yak warm as soon as possible, the delivery personnel should cut the umbilical cord in time, squeeze the blood and mucus in the umbilical cord, and disinfect with 5% iodine. The broken umbilical cord can be tied with a small buckle, which is naturally detached. The mucus on the yak body, mouth and nose should be removed with a towel as soon as possible. Second, after the yak is born, try to eat colostrum in half an hour. Colostrum contains more maternal antibodies that enhance the resistance of calves to disease. Weak calves need to be artificially assisted until they will eat milk. The third is to pay attention to the weaning time and reasonably match the yak feed. The yak began to train and supplement the yak compound feed in about 10 days. Try not to mix the yak feed. You should buy the full-price yak feed from the regular feed manufacturer. Yaks gradually feed on soft grass to promote rumen development. Under normal circumstances, the yak can be weaned for 2 months, and it is recommended to extend the weaning period to 2.5 to 3 months in the winter in the southwestern mountainous area. The yak weaning should have a transition period, gradually reduce the number of feedings every day, increase the amount of supplementary feeding and drinking water, and use the weaning method of cows leaving the ring and keeping the yak in the ring.
Fourth, early deworming
After the stocking of the beef cattle in autumn, the parasites in the cattle need to be completely slain before wintering to ensure the cattle are safely wintering. Aphids, flukes of the liver, mites, burdock, burdock, burdock, etc. are common parasites in cattle and on the body surface. If there are clinical symptoms, it is necessary to judge the type of parasites and select high-efficiency and low-toxic deworming drugs. At present, there are many kinds of anthelmintic drugs, and commonly used are albendazole, trichlorfon, levamisole, avermectin, ivermectin and the like. Abamectin and ivermectin are the preferred drugs for deworming. This drug is effective against a variety of nematodes (such as aphids) in cattle and in vitro parasites such as cockroaches, ticks, cockroaches, maggots, etc. according to different dosage forms. , filling and or subcutaneous injection in the neck. The drug of choice for killing flukes and mites is praziquantel. If the insect repellent is fed, in order to facilitate the absorption of the anthelmintic, the cattle need to be fasted for more than 12 hours before the deworming, and the anthelmintic and the feed are evenly mixed, and the feeding is completed at one time. After the deworming, the manure from the steak should be cleaned up and piled up for fermentation. The barn and the feeding trough should be disinfected with 5% lime water to kill the eggs that are driven out and prevent the second infection of the cattle. Pregnancy cows should be cautious when using deworming drugs. Select drugs that indicate the availability of pregnant animals. Under normal circumstances, it is not recommended to deworm during pregnancy to avoid abortion.
5. Environmental sanitation and disinfection
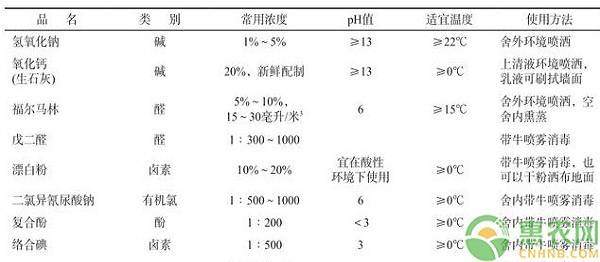
Winter is the high incidence period of foot-and-mouth disease. It is necessary to do the environmental sanitation and disinfection work inside and outside the barn: remove the manure of the pens and sports fields every day, keep the barn and sports ground clean, dry and hygienic; remove the snow and dirt around and keep it in time. The drainage ditch around the barn is smooth and clean; the icing on the barn and the sports ground is broken in time to prevent the cow from falling and the pregnant cow aborted. Regarding winter disinfection, there is a common misunderstanding in cattle farms. It is believed that winter temperatures are low and microbes are slow to breed. It can relax the disinfection of fields and equipment, especially the disinfection of yak and delivery rooms. In fact, the winter yak house and the delivery room are well closed, and the temperature inside the house is high, which provides favorable conditions for the breeding of pathogens. In addition, the winter is the season of foot-and-mouth disease virus, and the disinfection is not easy to cause yak and postpartum cattle. The correct way is: the area is fully disinfected once every 2 weeks, the cattle are disinfected once a week, and there are more than 3 different types of disinfectant drugs used in the cattle farm. The foot-and-mouth disease virus is sensitive to both acid and alkali, and its disinfecting drugs and methods of use are detailed in Table 2.
Table 2 Disinfectants commonly used in foot and mouth disease
For the wonderful pictures and popular comments on the wintering management technology of beef in the southwest mountain area, you may be interested in the following recommended contents. Welcome to read.
Pain Relief Patch(Pain Areas)
Pain Relief Patch
[Name] Medical Cold Patch
[Package Dimension] 6cm×8cm 4pieces/box
The pain relief patch is composed of three layers, namely, backing lining, middle gel and protective film. It is free from pharmacological, immunological or metabolic ingredients.
[Scope of Application]
For cold physiotherapy, closed soft tissue only.
[Indications]
The patches give fast acting pain relief for strains, sprains, cramp, bruises, swollen areas or joint stiffness.
[How To Use a Patch]
Please follow the Schematic Diagram. One piece, one time.
The curing effect of each piece can last for 6-8 hours.
[Attention]
Do not apply the patch on the problematic skin, such as wounds, eczema, dermatitis,or in the eyes. People allergic to herbs and the pregnant are advised not to use the medication. If swelling or irritation occurs, please stop using and if any of these effects persist or worsen.notify your doctor or pharmacist promptly. Children using the patch must be supervised by adults.
[Storage Conditions]
Store below 30c in a dry place away from heat and direct sunlight.
Pain Relief Patch(Pain Areas),Shouler Pain Relief Patch,Joints Pain Relief Patch, Muscle Pain Relief Patch
Shandong XiJieYiTong International Trade Co.,Ltd. , https://www.sdxjmedical.com