Bovine foot-and-mouth disease has the characteristics of rapid spread, acute onset, and high mortality. Therefore, farmers should pay enough attention to do a good job of immunization to reduce the probability of onset. So how do cattle foot-and-mouth disease judge and treat?
First, the clinical symptoms of beef foot and mouth disease
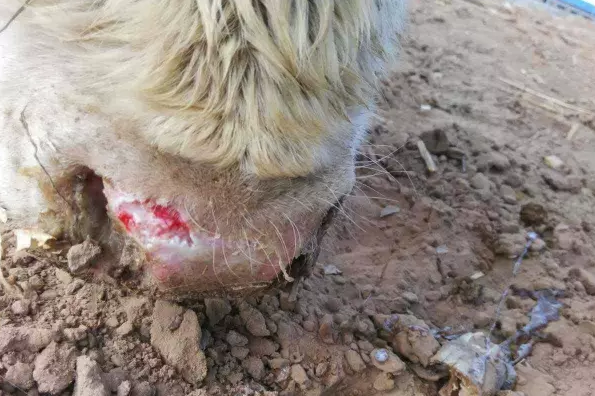
Bovine foot and mouth disease can be judged based on clinical symptoms. However, it is necessary to have an in-depth understanding of the disease. The incubation period of the cattle foot-and-mouth disease may be late for 3 to 4 days or more, and some may occur after 2 days. After infection with the foot-and-mouth disease, the cattle will have fever and other organs change, and a large number of blisters appear on the hooves, tongue and lips. If the blisters are not found to grow and rupture, the red spots are obviously festering. At the same time, the cow will have some systemic symptoms that do not eat grass, no spirit, no movement. There are also some differences in the performance of sick cows due to age. The younger the age, the heavier the disease and the higher the mortality rate.
Second, the spread of cattle foot and mouth disease
Usually sick cattle and latent infected cattle carry a large number of viruses. If it is not detected and isolated in time, it will easily cause the rapid spread of the disease. The large amount of virus in the faeces and saliva of these steaks poses a great threat to other herds. The disease is mainly caused by the digestive tract infection of cattle. Related studies have found that the disease is more common in spring. In addition, the role of the wind and the migration of birds have also increased the trend.
Third, the prevention and control measures of cattle foot and mouth disease
1. Put the epidemic prevention work seriously
We must conscientiously implement the epidemic prevention system, strengthen prevention and control, and do our utmost to control the spread and spread of the foot-and-mouth disease. Strengthen the sanitation and epidemic prevention of the cattle house and carry out comprehensive cleaning. Use disinfection measures to disinfect the pens and keep the pens clean, and concentrate the cattle manure to do epidemic prevention work. To prevent the transmission of pathogenic bacteria, physical disinfection and chemical disinfection at the same time to achieve all-round no dead angle, to ensure the effectiveness and quality of epidemic prevention.
2. Establish a strict system for prevention and control of beef foot-and-mouth disease
Relevant management departments should pay sufficient attention to this work. Although the disease has not been found to be infected, the cattle-cow transmission is very serious and very destructive. The responsible person in charge of this responsibility should strengthen the monitoring of the importance of the disease, implement the system's improvement and implementation, and clarify the responsibility to improve the level of prevention and treatment.
3. Strengthen quarantine measures and focus on strengthening quarantine of import and sale links
In accordance with the relevant system regulations, the quarantine work was seriously implemented, the inspection of the cattle-inducing and cattle-selling links was strengthened, and the quarantine efforts were strengthened to observe the work in the end. In order to prevent the introduction of sick cattle, we should also focus on testing the cattle selling link to avoid the flow of sick cattle into the market.
4, vaccination
Regular vaccination of cattle can effectively reduce the incidence of the disease, and do a good job in feeding management to ensure the healthy growth of cattle
5. Strengthen the epidemic control and reporting system
If the foot-and-mouth disease phenomenon occurs in the cattle house, it must be contacted with the superior quarantine department to report the situation, and then the department will send staff to analyze and study the specific situation, and take effective measures in time to control the epidemic to avoid its spread. With the spread.
6, epidemic prevention measures must be appropriate
If it is found that the sick cattle should strengthen the isolation measures, strictly control the living and active areas of the sick cattle, and strengthen the management of all unrelated personnel and cattle. Moreover, it is necessary to strengthen market supervision to prevent sick cattle from entering the market. The area where the sick cow has lived must be strictly disinfected to achieve seamless coverage. Remove the hair and feces that have fallen off to avoid carrying the bacteria. After the emergence of no new foot-and-mouth disease cattle in the area, and all the sick cattle have been well cured, it can be considered that the epidemic is effectively controlled after more than half a month of practice.

7. Strengthen the management of sick cattle
Foot-and-mouth disease has always been one of the main diseases of cattle farmers' economic losses. Over the years, the majority of farmers have been fighting against it. Prevention of foot-and-mouth disease should do the following work:
(1) Segregation should be done to effectively isolate sick cattle from normal cattle, and attention should also be paid to the impact of environmental changes on sick cattle.
(2) Ensure that the enclosure is clean, adequately lit, temperature is appropriate, and excessive interference is avoided to adversely affect it. Efforts to keep the barn consistent with the usual usual, and to add some straw to the barn to pave the way to make the cattle more comfortable.
(3) Strengthen feed replenishment and add some vitamin-rich feed. The feed should be changed to liquid food, nutrition should be balanced, and the proper structure of the feed should ensure the nutrition of the food is sufficient, and avoid the malnutrition of the cattle due to unreasonable nutrition.
(4) Prevention and treatment of beef foot-and-mouth disease: The current serum can be well controlled. If ulceration has occurred, it can be applied externally. Potassium permanganate can be used to treat the affected area, and it can be recovered by using it twice a day for 15~20 days. At the same time of treatment, the affected area cannot be stuck to water or contaminated, so as not to cause more serious harm to the cure of the disease.
Bovine foot-and-mouth disease is one of the most serious diseases in the world. Therefore, farmers should not relax the epidemic prevention work, strengthen the scientific management of cattle and take effective preventive measures to reduce the chance of contracting the disease.
FOSHAN PHARMA CO., LTD. , https://www.fspharmamedicine.com